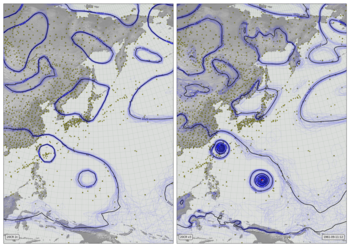
Observations coverage video¶
In each 1x1 degree grid-cell, a bright yellow circle is shown if at least one pressure observation is available every 6 hours (one in each assimilation run). Paler yellow circles indicate observations in some, but not all assimilation periods (partial coverage). Each frame covers a 10-day period.
Code to make the figure¶
Script to make an individual frame - takes year, month, day, and hour as command-line options:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Observations coverage in 20CRv3
import os
import datetime
import iris
import numpy
import pandas
import matplotlib
from matplotlib.backends.backend_agg import FigureCanvasAgg as FigureCanvas
from matplotlib.figure import Figure
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
# Fix dask SPICE bug
import dask
dask.config.set(scheduler='single-threaded')
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--year", help="Year",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--month", help="Integer month",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--day", help="Day of month",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--hour", help="Time of day (0 to 23.99)",
default=12,
type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--opdir", help="Directory for output files",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_observations" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
if not os.path.isdir(args.opdir):
os.makedirs(args.opdir)
dte=datetime.datetime(args.year,args.month,args.day,
int(args.hour),int(args.hour%1*60))
def load_observations_1file(of_name):
compression='infer'
if of_name[-2:]=='gz': compression='gzip'
o=pandas.read_fwf(of_name,
colspecs=[(0,19),
(20,50),
(52,64),
(66,68),
(69,72),
(74,80),
(81,87),
(88,95),
(97,102),
(103,110),
(111,112),
(113,123),
(124,134),
(135,145),
(146,156),
(157,167),
(168,175),
(176,183),
(184,191),
(192,200),
(201,205),
(206,213),
(214,221),
(222,223)],
header=None,
encoding="ISO-8859-1",
compression=compression,
usecols=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6],
names=['UID',
'Name',
'ID',
'Type',
'NCEP.Type',
'Longitude',
'Latitude',
'Observed',
'Time.offset',
'Observed.2',
'Skipped',
'Bias.correction',
'Obfit.prior',
'Obfit.post',
'Obsprd.prior',
'Obsprd.post',
'Oberrvar.orig.out',
'Oberrvar.out',
'Oberrvar.use',
'Paoverpb.save',
'Prob.gross.error',
'Localization.length.scale',
'Lnsigl',
'QC.failure.flag'],
converters={'UID': str,
'Name': str,
'ID': str,
'Type': str,
'NCEP.Type': str,
'Longitude': float,
'Latitude': float,
'Observed': float,
'Time.offset': float,
'Observed.2': float,
'Skipped': int,
'Bias.correction': float,
'Obfit.prior': float,
'Obfit.post': float,
'Obsprd.prior': float,
'Obsprd.post': float,
'Oberrvar.orig.out': float,
'Oberrvar.out': float,
'Oberrvar.use': float,
'Paoverpb.save': float,
'Prob.gross.error': float,
'Localization.length.scale': float,
'Lnsigl': float,
'QC.failure.flag': int},
na_values=['NA','*','***','*****','*******','**********',
'-99','9999','-999','9999.99','10000.0',
'-9.99',
'999999999999','9'],
comment=None)
return(o)
# Load the obs for +-15 days around given datetime
# Get the fraction of assimilation points with at least
# 1 ob for each 1x1 degree grid-cell.
n_fields=0
width=360
height=180
xmin=-180
xmax=180
ymin=-90
ymax=90
n_obs=numpy.zeros([width,height])
def x_to_i(x):
return numpy.minimum(width-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin)*(width-1)))).astype(int)
def y_to_j(y):
return numpy.minimum(height-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((y-ymin)/(ymax-ymin)*(height-1)))).astype(int)
def i_to_x(i):
return xmin + ((i+1)/width) * (xmax-xmin)
def j_to_y(j):
return ymin + ((j+1)/height) * (ymax-ymin)
ct=dte-datetime.timedelta(days=15)
et=dte+datetime.timedelta(days=15)
while ct<et:
if ct.hour%6==0:
ofile="%s/20CR/version_3/v3_observations/%04d/%04d%02d%02d%02d_psobs_posterior.txt" % (
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),ct.year,ct.year,ct.month,ct.day,ct.hour)
if not os.path.isfile(ofile):
ofile+='.gz'
obs=load_observations_1file(ofile)
longs=numpy.array(obs['Longitude'])
lats=numpy.array(obs['Latitude'])
w=((numpy.isfinite(longs)) & (numpy.isfinite(lats)) &
(longs>=xmin) & (longs <=360) &
(lats>=ymin) & (lats <=ymax))
longs=longs[w]
lats=lats[w]
longs[longs>180] -= 360
lon_i=x_to_i(longs)
lat_i=y_to_j(lats)
n_add=numpy.zeros([width,height])
for i in range(len(lon_i)):
n_add[lon_i[i],lat_i[i]] = 1
n_obs += n_add
n_fields += 1
ct += datetime.timedelta(hours=1)
n_obs /= n_fields
# Load a land mask
mask = iris.load_cube("%s/fixed_fields/land_mask/opfc_global_2019.nc" % os.getenv('DATADIR'))
# Define the figure (page size, background color, resolution, ...
fig=Figure(figsize=(19.2,10.8), # Width, Height (inches)
dpi=100,
facecolor=(0.5,0.5,0.5,1),
edgecolor=None,
linewidth=0.0,
frameon=False, # Don't draw a frame
subplotpars=None,
tight_layout=None)
fig.set_frameon(False)
# Attach a canvas
canvas=FigureCanvas(fig)
# Projection for plotting
cs=iris.coord_systems.RotatedGeogCS(90,180,0)
def plot_cube(resolution):
lat_values=numpy.arange(ymin,ymax+resolution,resolution)
latitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lat_values,
standard_name='latitude',
units='degrees_north',
coord_system=cs)
lon_values=numpy.arange(xmin,xmax+resolution,resolution)
longitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lon_values,
standard_name='longitude',
units='degrees_east',
coord_system=cs)
dummy_data = numpy.zeros((len(lat_values), len(lon_values)))
plot_cube = iris.cube.Cube(dummy_data,
dim_coords_and_dims=[(latitude, 0),
(longitude, 1)])
return plot_cube
# Define an axes to contain the plot. In this case our axes covers
# the whole figure
ax = fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1])
ax.set_axis_off() # Don't want surrounding x and y axis
# Lat and lon range (in rotated-pole coordinates) for plot
ax.set_xlim(xmin,xmax)
ax.set_ylim(ymin,ymax)
ax.set_aspect('auto')
# Background
ax.add_patch(Rectangle((xmin,ymin),width,height,facecolor=(0.5,0.5,0.5,1),fill=True,zorder=1))
# Draw lines of latitude and longitude
for lat in range(-90,95,5):
lwd=0.25
x=[]
y=[]
for lon in range(-180,181,1):
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(lon),
numpy.array(lat),
180,
90)
nx=rp[0]
if nx>180: nx -= 360
ny=rp[1]
if(len(x)==0 or (abs(nx-x[-1])<10 and abs(ny-y[-1])<10)):
x.append(nx)
y.append(ny)
else:
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
x=[]
y=[]
if(len(x)>1):
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
for lon in range(-180,185,5):
lwd=0.25
x=[]
y=[]
for lat in range(-90,90,1):
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(lon),
numpy.array(lat),
180,
90)
nx=rp[0]
if nx>180: nx -= 360
ny=rp[1]
if(len(x)==0 or (abs(nx-x[-1])<10 and abs(ny-y[-1])<10)):
x.append(nx)
y.append(ny)
else:
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
x=[]
y=[]
if(len(x)>1):
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
# Plot the land mask
mask_pc=plot_cube(0.05)
mask = mask.regrid(mask_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
lats = mask.coord('latitude').points
lons = mask.coord('longitude').points
mask_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, mask.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(
((0,0,0,0),
(0,0,0,1))),
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
alpha=1.0,
zorder=20)
# Plot the observations locations
for i in range(width):
for j in range(height):
if n_obs[i,j]==0: continue
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(i_to_x(i)),
numpy.array(j_to_y(j)),
180,
90)
nlon=rp[0][0]
nlat=rp[1][0]
ax.add_patch(matplotlib.patches.Circle((nlon,nlat),
radius=0.49,
facecolor='yellow',
edgecolor='yellow',
linewidth=0.1,
alpha=max(0.15,n_obs[i,j]),
zorder=180))
# Label with the date
ax.text(xmax-width*0.009,
ymax-height*0.016,
"%04d-%02d" % (args.year,args.month),
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='top',
color='black',
bbox=dict(facecolor=(0.8,0.8,0.8,0.5),
edgecolor='black',
boxstyle='round',
pad=0.5),
size=14,
clip_on=True,
zorder=500)
# Render the figure as a png
fig.savefig('%s/%04d%02d%02d.png' % (args.opdir,args.year,
args.month,args.day))
To make the video, it is necessary to run the script above hundreds of times - giving an image for every 10-day period. This script makes the list of commands needed to make all the images, which can be run in parallel.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Make all the individual frames for a movie
import os
import subprocess
import datetime
# Where to put the output files
opdir="%s/slurm_output" % os.getenv('SCRATCH')
if not os.path.isdir(opdir):
os.makedirs(opdir)
# Function to check if the job is already done for this timepoint
def is_done(year,month,day):
op_file_name=("%s/images/20CRv3_observations/" +
"%04d%02d%02d.png") % (
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
year,month,day)
if os.path.isfile(op_file_name):
return True
return False
f=open("run.txt","w+")
start_day=datetime.datetime(1851, 1, 1, 0)
end_day =datetime.datetime(2015, 12, 31, 23)
current_day=start_day
while current_day<=end_day:
if is_done(current_day.year,current_day.month,
current_day.day):
current_day=current_day+datetime.timedelta(days=10)
continue
cmd=("./plot_obs_coverage.py --year=%d --month=%d " +
"--day=%d "+
"\n") % (
current_day.year,current_day.month,
current_day.day)
f.write(cmd)
current_day=current_day+datetime.timedelta(days=10)
f.close()
To turn the thousands of images into a movie, use ffmpeg
ffmpeg -r 24 -pattern_type glob -i 20CRv3_observations/\*.png \
-c:v libx264 -threads 16 -preset veryslow -tune film \
-profile:v high -level 4.2 -pix_fmt yuv420p \
-b:v 5M -maxrate 5M -bufsize 20M \
-c:a copy 20CRv3_observations.mp4