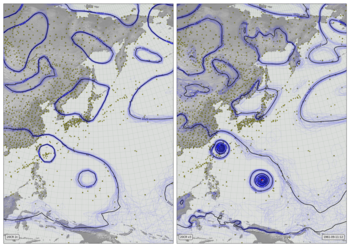
Weather and fog in 1903¶
Near-surface air temperature (2m - colours), 10m wind (vectors), and precipitation (green shading) from Version 3 of the Twentieth Century Reanalysis (first ensemble member). Black dots mark observations assimilated (of surface pressure), and the grey fog masks regions where the reanalysis is very uncertain (where the ensemble spread in sea-level pressure is not much smaller than the climatological variation).
Code to make the figure¶
Script to make an individual frame - takes year, month, day, and hour as command-line options:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Atmospheric state - near-surface temperature, wind, and precip.
import os
import IRData.opfc as opfc
import IRData.twcr as twcr
import datetime
import pickle
import iris
import numpy
import math
import matplotlib
from matplotlib.backends.backend_agg import FigureCanvasAgg as FigureCanvas
from matplotlib.figure import Figure
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
from pandas import qcut
# Fix dask SPICE bug
import dask
dask.config.set(scheduler='single-threaded')
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--year", help="Year",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--month", help="Integer month",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--day", help="Day of month",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--hour", help="Time of day (0 to 23.99)",
type=float,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--pole_latitude", help="Latitude of projection pole",
default=90,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--pole_longitude", help="Longitude of projection pole",
default=180,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--npg_longitude", help="Longitude of view centre",
default=0,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--zoom", help="Scale factor for viewport (1=global)",
default=1,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--opdir", help="Directory for output files",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_global_3var" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--zfile", help="Noise pickle file name",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_global_3var/z.pkl" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
if not os.path.isdir(args.opdir):
os.makedirs(args.opdir)
dte=datetime.datetime(args.year,args.month,args.day,
int(args.hour),int(args.hour%1*60))
# Remap the precipitation to standardise the distribution
# Normalise a precip field to fixed quantiles
def normalise_precip(p):
res=p.copy()
res.data[res.data<=2.00e-5]=0.79
res.data[res.data<2.10e-5]=0.81
res.data[res.data<2.50e-5]=0.83
res.data[res.data<3.10e-5]=0.85
res.data[res.data<3.80e-5]=0.87
res.data[res.data<4.90e-5]=0.89
res.data[res.data<6.60e-5]=0.91
res.data[res.data<9.10e-5]=0.93
res.data[res.data<13.4e-5]=0.95
res.data[res.data<22.0e-5]=0.97
res.data[res.data<0.79]=0.99
return res
# Remap the temperature similarly
def normalise_t2m(p):
res=p.copy()
res.data[res.data>300.10]=0.95
res.data[res.data>299.9]=0.90
res.data[res.data>298.9]=0.85
res.data[res.data>297.5]=0.80
res.data[res.data>295.7]=0.75
res.data[res.data>293.5]=0.70
res.data[res.data>290.1]=0.65
res.data[res.data>287.6]=0.60
res.data[res.data>283.7]=0.55
res.data[res.data>280.2]=0.50
res.data[res.data>277.2]=0.45
res.data[res.data>274.4]=0.40
res.data[res.data>272.3]=0.35
res.data[res.data>268.3]=0.30
res.data[res.data>261.4]=0.25
res.data[res.data>254.6]=0.20
res.data[res.data>249.1]=0.15
res.data[res.data>244.9]=0.10
res.data[res.data>240.5]=0.05
res.data[res.data>0.95]=0.0
return res
# Scale down the latitudinal variation in temperature
def damp_lat(sst,factor=0.25):
s=sst.shape
mt=numpy.min(sst.data)
for lat_i in range(s[0]):
lmt=numpy.mean(sst.data[lat_i,:])
if numpy.isfinite(lmt):
sst.data[lat_i,:] -= (lmt-mt)*factor
return(sst)
# Load the model data - dealing sensibly with missing fields
t2m=twcr.load('air.2m',dte,version='4.5.1')
t2m=t2m.extract(iris.Constraint(member=1))
t2m=normalise_t2m(t2m)
# Damp the latitude variation
t2m=damp_lat(t2m,factor=0.25)
u10m=twcr.load('uwnd.10m',dte,version='4.5.1')
u10m=u10m.extract(iris.Constraint(member=1))
v10m=twcr.load('vwnd.10m',dte,version='4.5.1')
v10m=v10m.extract(iris.Constraint(member=1))
icec=twcr.load('icec',dte,version='4.5.1')
icec=icec.extract(iris.Constraint(member=1))
precip=twcr.load('prate',dte,version='4.5.1')
precip=precip.extract(iris.Constraint(member=1))
prmsl=twcr.load('prmsl',dte,version='4.5.1')
prmsl=prmsl.collapsed('member',iris.analysis.STD_DEV)
precip=normalise_precip(precip)
obs=twcr.load_observations_fortime(dte,version='4.5.1')
dte1=datetime.datetime(2018,12,25,12)
try:
mask=opfc.load('lsmask',dte1,model='global')
except:
mask=opfc.load('lsmask',dte1-datetime.timedelta(days=1),model='global')
# Load the climatological prmsl stdev from v2c
prevt=datetime.datetime(args.year,args.month,args.day,
int(args.hour)-int(args.hour)%6)
prevcsd=iris.load_cube('/data/users/hadpb/20CR/version_3.4.1/standard.deviation/prmsl.nc',
iris.Constraint(time=iris.time.PartialDateTime(year=1981,
month=prevt.month,
day=prevt.day,
hour=prevt.hour)))
nextt=prevt+datetime.timedelta(hours=6)
nextcsd=iris.load_cube('/data/users/hadpb/20CR/version_3.4.1/standard.deviation/prmsl.nc',
iris.Constraint(time=iris.time.PartialDateTime(year=1981,
month=nextt.month,
day=nextt.day,
hour=nextt.hour)))
w=(dte-prevt).total_seconds()/(nextt-prevt).total_seconds()
prevcsd.data=prevcsd.data*(1-w)+nextcsd.data*w
coord_s=iris.coord_systems.GeogCS(iris.fileformats.pp.EARTH_RADIUS)
prevcsd.coord('latitude').coord_system=coord_s
prevcsd.coord('longitude').coord_system=coord_s
# Define the figure (page size, background color, resolution, ...
fig=Figure(figsize=(19.2,10.8), # Width, Height (inches)
dpi=100,
facecolor=(0.5,0.5,0.5,1),
edgecolor=None,
linewidth=0.0,
frameon=False, # Don't draw a frame
subplotpars=None,
tight_layout=None)
fig.set_frameon(False)
# Attach a canvas
canvas=FigureCanvas(fig)
# Projection for plotting
cs=iris.coord_systems.RotatedGeogCS(args.pole_latitude,
args.pole_longitude,
args.npg_longitude)
def plot_cube(resolution,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax):
lat_values=numpy.arange(ymin,ymax+resolution,resolution)
latitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lat_values,
standard_name='latitude',
units='degrees_north',
coord_system=cs)
lon_values=numpy.arange(xmin,xmax+resolution,resolution)
longitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lon_values,
standard_name='longitude',
units='degrees_east',
coord_system=cs)
dummy_data = numpy.zeros((len(lat_values), len(lon_values)))
plot_cube = iris.cube.Cube(dummy_data,
dim_coords_and_dims=[(latitude, 0),
(longitude, 1)])
return plot_cube
# Make the wind noise
def wind_field(uw,vw,zf,sequence=None,iterations=50,epsilon=0.003,sscale=1):
# Random field as the source of the distortions
z=pickle.load(open( zf, "rb" ) )
z=z.regrid(uw,iris.analysis.Linear())
(width,height)=z.data.shape
# Each point in this field has an index location (i,j)
# and a real (x,y) position
xmin=numpy.min(uw.coords()[0].points)
xmax=numpy.max(uw.coords()[0].points)
ymin=numpy.min(uw.coords()[1].points)
ymax=numpy.max(uw.coords()[1].points)
# Convert between index and real positions
def i_to_x(i):
return xmin + (i/width) * (xmax-xmin)
def j_to_y(j):
return ymin + (j/height) * (ymax-ymin)
def x_to_i(x):
return numpy.minimum(width-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin)*(width-1)))).astype(int)
def y_to_j(y):
return numpy.minimum(height-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((y-ymin)/(ymax-ymin)*(height-1)))).astype(int)
i,j=numpy.mgrid[0:width,0:height]
x=i_to_x(i)
y=j_to_y(j)
# Result is a distorted version of the random field
result=z.copy()
# Repeatedly, move the x,y points according to the vector field
# and update result with the random field at their locations
ss=uw.copy()
ss.data=numpy.sqrt(uw.data**2+vw.data**2)
if sequence is not None:
startsi=numpy.arange(0,iterations,3)
endpoints=numpy.tile(startsi,1+(width*height)//len(startsi))
endpoints += sequence%iterations
endpoints[endpoints>=iterations] -= iterations
startpoints=endpoints-25
startpoints[startpoints<0] += iterations
endpoints=endpoints[0:(width*height)].reshape(width,height)
startpoints=startpoints[0:(width*height)].reshape(width,height)
else:
endpoints=iterations+1
startpoints=-1
for k in range(iterations):
x += epsilon*vw.data[i,j]
x[x>xmax]=xmax
x[x<xmin]=xmin
y += epsilon*uw.data[i,j]
y[y>ymax]=y[y>ymax]-ymax+ymin
y[y<ymin]=y[y<ymin]-ymin+ymax
i=x_to_i(x)
j=y_to_j(y)
update=z.data*ss.data/sscale
update[(endpoints>startpoints) & ((k>endpoints) | (k<startpoints))]=0
update[(startpoints>endpoints) & ((k>endpoints) & (k<startpoints))]=0
result.data[i,j] += update
return result
wind_pc=plot_cube(0.2,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
rw=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_winds(u10m,v10m,cs)
u10m = rw[0].regrid(wind_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
v10m = rw[1].regrid(wind_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
seq=(dte-datetime.datetime(2000,1,1)).total_seconds()/3600
wind_noise_field=wind_field(u10m,v10m,args.zfile,sequence=int(seq*5),epsilon=0.01)
# Define an axes to contain the plot. In this case our axes covers
# the whole figure
ax = fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1])
ax.set_axis_off() # Don't want surrounding x and y axis
# Lat and lon range (in rotated-pole coordinates) for plot
ax.set_xlim(-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom)
ax.set_ylim(-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
ax.set_aspect('auto')
# Background
ax.add_patch(Rectangle((0,0),1,1,facecolor=(0.6,0.6,0.6,1),fill=True,zorder=1))
# Draw lines of latitude and longitude
for lat in range(-90,95,5):
lwd=0.75
x=[]
y=[]
for lon in range(-180,181,1):
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(lon),
numpy.array(lat),
args.pole_longitude,
args.pole_latitude)
nx=rp[0]+args.npg_longitude
if nx>180: nx -= 360
ny=rp[1]
if(len(x)==0 or (abs(nx-x[-1])<10 and abs(ny-y[-1])<10)):
x.append(nx)
y.append(ny)
else:
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
x=[]
y=[]
if(len(x)>1):
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
for lon in range(-180,185,5):
lwd=0.75
x=[]
y=[]
for lat in range(-90,90,1):
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(lon),
numpy.array(lat),
args.pole_longitude,
args.pole_latitude)
nx=rp[0]+args.npg_longitude
if nx>180: nx -= 360
ny=rp[1]
if(len(x)==0 or (abs(nx-x[-1])<10 and abs(ny-y[-1])<10)):
x.append(nx)
y.append(ny)
else:
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
x=[]
y=[]
if(len(x)>1):
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
# Plot the land mask
mask_pc=plot_cube(0.05,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
mask = mask.regrid(mask_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
lats = mask.coord('latitude').points
lons = mask.coord('longitude').points
mask_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, mask.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(
((0.4,0.4,0.4,0),
(0.4,0.4,0.4,1))),
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
alpha=1.0,
zorder=20)
# Plot the sea-ice
ice_pc=plot_cube(0.05,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
icec = icec.regrid(ice_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
icec_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, icec.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(
((0.5,0.5,0.5,0),
(0.5,0.5,0.5,1))),
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
alpha=1.0,
zorder=10)
# Plot the T2M
t2m_pc=plot_cube(0.05,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
t2m = t2m.regrid(t2m_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
# Adjust to show the wind
wscale=200
s=wind_noise_field.data.shape
wind_noise_field.data=qcut(wind_noise_field.data.flatten(),wscale,labels=False,
duplicates='drop').reshape(s)-(wscale-1)/2
# Plot as a colour map
wnf=wind_noise_field.regrid(t2m,iris.analysis.Linear())
t2m_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, t2m.data*1000+wnf.data,
cmap='RdYlBu_r',
alpha=0.8,
zorder=100)
# Plot the precip
precip_pc=plot_cube(0.25,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
precip = precip.regrid(precip_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
wnf=wind_noise_field.regrid(precip,iris.analysis.Linear())
precip.data[precip.data>0.8] += wnf.data[precip.data>0.8]/3000
precip.data[precip.data<0.8] = 0.8
cols=[]
for ci in range(100):
cols.append([0.0,0.3,0.0,ci/100])
precip_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, precip.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(cols),
alpha=0.9,
zorder=200)
# Plot the observations
for i in range(0,len(obs['Longitude'].values)):
weight=0.85
if 'weight' in obs.columns: weight=obs['weight'].values[i]
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(obs['Longitude'].values[i]),
numpy.array(obs['Latitude'].values[i]),
args.pole_longitude,
args.pole_latitude)
nlon=rp[0][0]
nlat=rp[1][0]
ax.add_patch(matplotlib.patches.Circle((nlon,nlat),
radius=0.4,
facecolor='black',
edgecolor='black',
linewidth=0.1,
alpha=weight,
zorder=180))
# Plot the fog of ignorance
fog_pc=plot_cube(0.25,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
prmsl = prmsl.regrid(precip_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
prevcsd = prevcsd.regrid(precip_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
prmsl.data = numpy.minimum(1,prmsl.data/prevcsd.data)
cols=[]
def fog_map(x):
return 1/(1+math.exp((x-0.5)*-10))
for ci in range(100):
cols.append([0.8,0.8,0.8,fog_map(ci/100)])
fog_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, prmsl.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(cols),
alpha=0.95,
zorder=300)
# Label with the date
ax.text(180/args.zoom-(360/args.zoom)*0.009,
90/args.zoom-(180/args.zoom)*0.016,
"%04d-%02d-%02d" % (args.year,args.month,args.day),
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='top',
color='black',
bbox=dict(facecolor=(0.6,0.6,0.6,0.5),
edgecolor='black',
boxstyle='round',
pad=0.5),
size=14,
clip_on=True,
zorder=500)
# Render the figure as a png
fig.savefig('%s/%04d%02d%02d%02d%02d.png' % (args.opdir,args.year,
args.month,args.day,
int(args.hour),
int(args.hour%1*60)))
That script uses a random noise field to generate the wind vectors, and we want every frame to use the same noise field, so make and store that.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Make a fixed noise field for wind-map plots.
import os
import iris
import numpy
import pickle
import os
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--resolution", help="Resolution for plot grid",
default=0.1,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--zoom", help="Scale factor for viewport (1=global)",
default=1,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--opfile", help="Output (pickle) file name",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_global_3var/z.pkl" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
# Nominal projection
cs=iris.coord_systems.RotatedGeogCS(90,180,0)
def plot_cube(resolution,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax):
lat_values=numpy.arange(ymin,ymax+resolution,resolution)
latitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lat_values,
standard_name='latitude',
units='degrees_north',
coord_system=cs)
lon_values=numpy.arange(xmin,xmax+resolution,resolution)
longitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lon_values,
standard_name='longitude',
units='degrees_east',
coord_system=cs)
dummy_data = numpy.zeros((len(lat_values), len(lon_values)))
plot_cube = iris.cube.Cube(dummy_data,
dim_coords_and_dims=[(latitude, 0),
(longitude, 1)])
return plot_cube
z=plot_cube(args.resolution,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
(width,height)=z.data.shape
z.data=numpy.random.rand(width,height)-0.5
z2=plot_cube(args.resolution*2,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
(width,height)=z2.data.shape
z2.data=numpy.random.rand(width,height)-0.5
z2=z2.regrid(z,iris.analysis.Linear())
z.data=z.data+z2.data
z4=plot_cube(args.resolution*4,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
(width,height)=z4.data.shape
z4.data=numpy.random.rand(width,height)-0.5
z4=z4.regrid(z,iris.analysis.Linear())
z.data=z.data+z4.data*100
pickle.dump( z, open( args.opfile, "wb" ) )
To make the video, it is necessary to run the frame generation script above hundreds of times - giving an image for every hour. This script makes the list of commands needed to make all the images, which can be run in parallel.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Make all the individual frames for a movie
import os
import subprocess
import datetime
# Where to put the output files
opdir="%s/slurm_output" % os.getenv('SCRATCH')
if not os.path.isdir(opdir):
os.makedirs(opdir)
# Function to check if the job is already done for this timepoint
def is_done(year,month,day,hour):
op_file_name=("%s/images/20CRv3_global_3var/" +
"%04d%02d%02d%02d%02d.png") % (
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
year,month,day,int(hour),
int(hour%1*60))
if os.path.isfile(op_file_name):
return True
return False
f=open("run.txt","w+")
start_day=datetime.datetime(1903, 1, 1, 0)
end_day =datetime.datetime(1903, 12, 31, 23)
current_day=start_day
while current_day<=end_day:
if is_done(current_day.year,current_day.month,
current_day.day,current_day.hour+current_day.minute/60):
current_day=current_day+datetime.timedelta(hours=1)
continue
cmd=("./20CRv3_3var.py --year=%d --month=%d " +
"--day=%d --hour=%f "+
"--pole_latitude=90 --pole_longitude=180 "+
"--npg_longitude=0 "+
"--zoom=1 "+
"\n") % (
current_day.year,current_day.month,
current_day.day,current_day.hour+current_day.minute/60)
f.write(cmd)
current_day=current_day+datetime.timedelta(hours=1)
f.close()
To turn the thousands of images into a movie, use ffmpeg
ffmpeg -r 24 -pattern_type glob -i 20CRv3_global_3var/\*.png \
-c:v libx264 -threads 16 -preset veryslow -tune film \
-profile:v high -level 4.2 -pix_fmt yuv420p \
-b:v 5M -maxrate 5M -bufsize 20M \
-c:a copy 20CRv3_global_3var.mp4