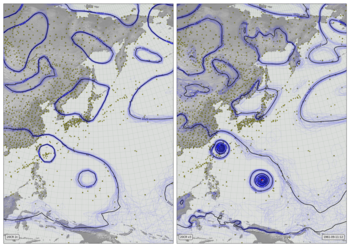
Weather and fog 1850-2015¶
Near-surface air temperature (2m - colours), 10m wind (vectors), and precipitation (green shading) from Version 3 of the Twentieth Century Reanalysis (first ensemble member). Black dots mark observations assimilated (of surface pressure), and the grey fog masks regions where the reanalysis is very uncertain (where the ensemble spread in sea-level pressure is not much smaller than the climatological variation).
To show the full period at this speed would produce almost 17 hours of video, so this is a sample: after showing 10 days of weather, the video jumps forward in time about 10 years.
Code to make the figure¶
This video is expensive in its data requirements: you have to download the full ensemble, for four variables, for each year included. That’s about 5Tb of data. You also need temperature normals, and MSLP ensemble spreads, but that’s a much smaller quantity.
Script to download the ensemble data:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import datetime
import IRData.twcr as twcr
start = datetime.date(1850,1,1)
end = datetime.date(2015,12,31)
yrs=[]
current = start
count=0
last=None
while current<=end:
if last is None or current.year != last:
yrs.append(current.year)
last = current.year
count = count+1
if count>=100:
count=0
if current.month==2 and current.day==29:
current += datetime.timedelta(days=1)
current = datetime.date(current.year+10,current.month,current.day)
current += datetime.timedelta(days=1)
for year in yrs:
for var in ('PRATE','UGRD10m','VGRD10m','TMP2m','PRMSL','observations'):
twcr.fetch(var,datetime.datetime(year,3,12,6),version='3')
Script to download the PRMSL ensemble spreads:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import datetime
import IRData.twcr as twcr
start = datetime.date(1850,1,1)
end = datetime.date(2015,12,31)
yrs=[]
current = start
count=0
last=None
while current<=end:
if last is None or current.year != last:
yrs.append(current.year)
last = current.year
count = count+1
if count>=100:
count=0
if current.month==2 and current.day==29:
current += datetime.timedelta(days=1)
current = datetime.date(current.year+10,current.month,current.day)
current += datetime.timedelta(days=1)
for year in yrs:
if year<1981:
print("wget ftp://ftp.cdc.noaa.gov/Datasets/20thC_ReanV3/spreads/miscSI/prmsl.%04d.nc" % year)
else:
print("wget ftp://ftp.cdc.noaa.gov/Datasets/20thC_ReanV3/spreads/miscMO/prmsl.%04d.nc" % year)
Script to make an individual frame - takes year, month, day, and hour as command-line options:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Atmospheric state - near-surface temperature, wind, and precip.
import os
import IRData.twcr as twcr
import datetime
import pickle
import iris
import numpy
import math
import matplotlib
from matplotlib.backends.backend_agg import FigureCanvasAgg as FigureCanvas
from matplotlib.figure import Figure
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
from pandas import qcut
# Fix dask SPICE bug
import dask
dask.config.set(scheduler='single-threaded')
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--year", help="Year",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--month", help="Integer month",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--day", help="Day of month",
type=int,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--hour", help="Time of day (0 to 23.99)",
type=float,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--pole_latitude", help="Latitude of projection pole",
default=90,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--pole_longitude", help="Longitude of projection pole",
default=180,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--npg_longitude", help="Longitude of view centre",
default=0,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--zoom", help="Scale factor for viewport (1=global)",
default=1,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--opdir", help="Directory for output files",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_time_skips" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--zfile", help="Noise pickle file name",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_time_skips/z.pkl" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
if not os.path.isdir(args.opdir):
os.makedirs(args.opdir)
dte=datetime.datetime(args.year,args.month,args.day,
int(args.hour),int(args.hour%1*60))
# Coordinate system to add to 20CR data
coord_s=iris.coord_systems.GeogCS(iris.fileformats.pp.EARTH_RADIUS)
# Remap the precipitation to standardise the distribution
# Normalise a precip field to fixed quantiles
def normalise_precip(p):
res=p.copy()
res.data[res.data<=2.00e-5]=0.79
res.data[res.data<2.10e-5]=0.81
res.data[res.data<2.50e-5]=0.83
res.data[res.data<3.10e-5]=0.85
res.data[res.data<3.80e-5]=0.87
res.data[res.data<4.90e-5]=0.89
res.data[res.data<6.60e-5]=0.91
res.data[res.data<9.10e-5]=0.93
res.data[res.data<13.4e-5]=0.95
res.data[res.data<22.0e-5]=0.97
res.data[res.data<0.79]=0.99
return res
# Remap the temperature similarly
def normalise_t2m(p):
res=p.copy()
res.data[res.data>300.10]=0.95
res.data[res.data>299.9]=0.90
res.data[res.data>298.9]=0.85
res.data[res.data>297.5]=0.80
res.data[res.data>295.7]=0.75
res.data[res.data>293.5]=0.70
res.data[res.data>290.1]=0.65
res.data[res.data>287.6]=0.60
res.data[res.data>283.7]=0.55
res.data[res.data>280.2]=0.50
res.data[res.data>277.2]=0.45
res.data[res.data>274.4]=0.40
res.data[res.data>272.3]=0.35
res.data[res.data>268.3]=0.30
res.data[res.data>261.4]=0.25
res.data[res.data>254.6]=0.20
res.data[res.data>249.1]=0.15
res.data[res.data>244.9]=0.10
res.data[res.data>240.5]=0.05
res.data[res.data>0.95]=0.0
return res
# Get normals and standard deviations
def get_normal(var,dte,startyear=1981,endyear=2010):
dstart = datetime.datetime(dte.year,dte.month,dte.day,dte.hour-dte.hour%3)
cday = dstart.day
if dstart.month==2 and dstart.day==29: cday=28
nstart=iris.load_cube(("%s/20CR/version_3/normals/%s/"+
"climatology_%04d_%04d/%02d%02d%02d.nc") % (
os.getenv('DATADIR'),var,
startyear,endyear,
dstart.month,cday,dstart.hour))
nstart.coord('latitude').coord_system=coord_s
nstart.coord('longitude').coord_system=coord_s
if dte.hour%3==0: return(nstart)
dend = dstart+datetime.timedelta(hours=3)
cday = dend.day
if dend.month==2 and dend.day==29: cday=28
nend=iris.load_cube(("%s/20CR/version_3/normals/%s/"+
"climatology_%04d_%04d/%02d%02d%02d.nc") % (
os.getenv('DATADIR'),var,
startyear,endyear,
dend.month,cday,dstart.hour))
# Can't use iris interpolation because it will mess up on leap days
weight = dte.hour%3/3
nstart.data = nend.data*weight + nstart.data*(1-weight)
return(nstart)
def get_sd(var,dte,startyear=1981,endyear=2010):
dstart = datetime.datetime(dte.year,dte.month,dte.day,dte.hour-dte.hour%3)
cday = dstart.day
if dstart.month==2 and dstart.day==29: cday=28
nstart=iris.load_cube(("%s/20CR/version_3/sds/%s/"+
"climatology_%04d_%04d/%02d%02d%02d.nc") % (
os.getenv('DATADIR'),var,
startyear,endyear,
dstart.month,cday,dstart.hour))
nstart.coord('latitude').coord_system=coord_s
nstart.coord('longitude').coord_system=coord_s
if dte.hour%3==0: return(nstart)
dend = dstart+datetime.timedelta(hours=3)
cday = dend.day
if dend.month==2 and dend.day==29: cday=28
nend=iris.load_cube(("%s/20CR/version_3/sds/%s/"+
"climatology_%04d_%04d/%02d%02d%02d.nc") % (
os.getenv('DATADIR'),var,
startyear,endyear,
dend.month,cday,dstart.hour))
# Can't use iris interpolation because it will mess up on leap days
weight = (dte.hour%3)/3
nstart.data = nend.data*weight + nstart.data*(1-weight)
return(nstart)
def get_spread_at_ts(var,dte):
if var=='PRMSL':
fname='prmsl'
vname='air_pressure_at_sea_level'
if var=='TMP2m':
fname='air.2m'
vname='air_temperature'
time_constraint=iris.Constraint(time=iris.time.PartialDateTime(
year=dte.year,
month=dte.month,
day=dte.day,
hour=dte.hour))
name_constraint=iris.Constraint(name=vname)
spread = iris.load_cube("%s/20CR/version_3/ensemble_spreads/%s/%s.%04d.nc" %
(os.getenv('SCRATCH'),var,fname,dte.year),
time_constraint & name_constraint)
spread.coord('latitude').coord_system=coord_s
spread.coord('longitude').coord_system=coord_s
return(spread)
def get_spread(var,dte):
dstart = datetime.datetime(dte.year,dte.month,dte.day,dte.hour-dte.hour%3)
nstart = get_spread_at_ts(var,dstart)
if dte.hour%3==0: return(nstart)
dend = dstart+datetime.timedelta(hours=3)
nend = get_spread_at_ts(var,dend)
weight = (dte.hour%3)/3
nstart.data = nend.data*weight + nstart.data*(1-weight)
return(nstart)
# Get current diurnal effect
def get_diurnal(var,dte):
current = twcr.load(var,dte,version='3',member=1)
start = dte-datetime.timedelta(hours=12)
for i in range(0,24,3):
dc = twcr.load(var,start+datetime.timedelta(hours=i),
version='3',member=1)
current.data = current.data-dc.data/8
return(current)
# Temperature
t = twcr.load('TMP2m',dte,version='3',member=1)
t_normal = get_normal('TMP2m',dte)
t_normal = t_normal.regrid(t,iris.analysis.Linear())
t_diurnal = get_diurnal('TMP2m',dte)
# Adjust the field to downplay diurnal variability and enhance
# weather variability
t -= t_diurnal*0.75
t += t-t_normal
# Normalise for plotting
t=normalise_t2m(t)
# Wind
u10m=twcr.load('UGRD10m',dte,version='3',member=1)
v10m=twcr.load('VGRD10m',dte,version='3',member=1)
# Precip
precip=twcr.load('PRATE',dte,version='3',member=1)
precip=normalise_precip(precip)
# Observations
width=360
height=180
xmin=-180
xmax=180
ymin=-90
ymax=90
def x_to_i(x):
return numpy.minimum(width-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin)*(width-1)))).astype(int)
def y_to_j(y):
return numpy.minimum(height-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((y-ymin)/(ymax-ymin)*(height-1)))).astype(int)
def i_to_x(i):
return xmin + ((i+1)/width) * (xmax-xmin)
def j_to_y(j):
return ymin + ((j+1)/height) * (ymax-ymin)
def get_obs(dte):
pr_obs=twcr.load_observations_fortime(dte,version='3')
pr_obs=pr_obs.dropna(subset=['Latitude', 'Longitude'])
pr_obs=pr_obs.reset_index(drop=True)
# Reduce the obs to 1-degree mean pseudo-obs
obs = numpy.ma.array(numpy.zeros([width,height]), mask = True)
counts = numpy.zeros([width,height])
pr_obs['Longitude'][pr_obs['Longitude']>180] -= 360
lon_i=x_to_i(pr_obs['Longitude'])
lat_i=y_to_j(pr_obs['Latitude'])
for i in range(len(lon_i)):
obs.mask[lon_i[i],lat_i[i]]=False
obs[lon_i[i],lat_i[i]] = max(obs[lon_i[i],lat_i[i]],pr_obs['weight'][i])
return(obs)
# PRMSL for fog, so only spread and sd
# Get a daily average, otherwise it flickers too much
def get_fog(dte):
prmsl=get_spread('PRMSL',dte)
prmsl_sd = get_sd('PRMSL',dte)
prmsl_sd = prmsl_sd.regrid(prmsl,iris.analysis.Linear())
prmsl.data = numpy.minimum(1,prmsl.data/prmsl_sd.data)
return(prmsl)
fog = get_spread('PRMSL',dte)
fog.data *=0
start = dte-datetime.timedelta(hours=12)
for i in range(0,24,3):
fog.data += get_fog(start+datetime.timedelta(hours=i)).data/8
# Land mask for plotting
mask=iris.load_cube("%s/fixed_fields/land_mask/opfc_global_2019.nc" % os.getenv('DATADIR'))
# Define the figure (page size, background color, resolution, ...
fig=Figure(figsize=(19.2,10.8), # Width, Height (inches)
dpi=100,
facecolor=(0.5,0.5,0.5,1),
edgecolor=None,
linewidth=0.0,
frameon=False, # Don't draw a frame
subplotpars=None,
tight_layout=None)
fig.set_frameon(False)
# Attach a canvas
canvas=FigureCanvas(fig)
# Projection for plotting
cs=iris.coord_systems.RotatedGeogCS(args.pole_latitude,
args.pole_longitude,
args.npg_longitude)
def plot_cube(resolution,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax):
lat_values=numpy.arange(ymin,ymax+resolution,resolution)
latitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lat_values,
standard_name='latitude',
units='degrees_north',
coord_system=cs)
lon_values=numpy.arange(xmin,xmax+resolution,resolution)
longitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lon_values,
standard_name='longitude',
units='degrees_east',
coord_system=cs)
dummy_data = numpy.zeros((len(lat_values), len(lon_values)))
plot_cube = iris.cube.Cube(dummy_data,
dim_coords_and_dims=[(latitude, 0),
(longitude, 1)])
return plot_cube
# Make the wind noise
def wind_field(uw,vw,zf,sequence=None,iterations=50,epsilon=0.003,sscale=1):
# Random field as the source of the distortions
z=pickle.load(open( zf, "rb" ) )
z=z.regrid(uw,iris.analysis.Linear())
(width,height)=z.data.shape
# Each point in this field has an index location (i,j)
# and a real (x,y) position
xmin=numpy.min(uw.coords()[0].points)
xmax=numpy.max(uw.coords()[0].points)
ymin=numpy.min(uw.coords()[1].points)
ymax=numpy.max(uw.coords()[1].points)
# Convert between index and real positions
def i_to_x(i):
return xmin + (i/width) * (xmax-xmin)
def j_to_y(j):
return ymin + (j/height) * (ymax-ymin)
def x_to_i(x):
return numpy.minimum(width-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin)*(width-1)))).astype(int)
def y_to_j(y):
return numpy.minimum(height-1,numpy.maximum(0,
numpy.floor((y-ymin)/(ymax-ymin)*(height-1)))).astype(int)
i,j=numpy.mgrid[0:width,0:height]
x=i_to_x(i)
y=j_to_y(j)
# Result is a distorted version of the random field
result=z.copy()
# Repeatedly, move the x,y points according to the vector field
# and update result with the random field at their locations
ss=uw.copy()
ss.data=numpy.sqrt(uw.data**2+vw.data**2)
if sequence is not None:
startsi=numpy.arange(0,iterations,3)
endpoints=numpy.tile(startsi,1+(width*height)//len(startsi))
endpoints += sequence%iterations
endpoints[endpoints>=iterations] -= iterations
startpoints=endpoints-25
startpoints[startpoints<0] += iterations
endpoints=endpoints[0:(width*height)].reshape(width,height)
startpoints=startpoints[0:(width*height)].reshape(width,height)
else:
endpoints=iterations+1
startpoints=-1
for k in range(iterations):
x += epsilon*vw.data[i,j]
x[x>xmax]=xmax
x[x<xmin]=xmin
y += epsilon*uw.data[i,j]
y[y>ymax]=y[y>ymax]-ymax+ymin
y[y<ymin]=y[y<ymin]-ymin+ymax
i=x_to_i(x)
j=y_to_j(y)
update=z.data*ss.data/sscale
update[(endpoints>startpoints) & ((k>endpoints) | (k<startpoints))]=0
update[(startpoints>endpoints) & ((k>endpoints) & (k<startpoints))]=0
result.data[i,j] += update
return result
wind_pc=plot_cube(0.2,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
rw=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_winds(u10m,v10m,cs)
u10m = rw[0].regrid(wind_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
v10m = rw[1].regrid(wind_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
seq=(dte-datetime.datetime(2000,1,1)).total_seconds()/3600
wind_noise_field=wind_field(u10m,v10m,args.zfile,sequence=int(seq*5),epsilon=0.01)
# Define an axes to contain the plot. In this case our axes covers
# the whole figure
ax = fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1])
ax.set_axis_off() # Don't want surrounding x and y axis
# Lat and lon range (in rotated-pole coordinates) for plot
ax.set_xlim(-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom)
ax.set_ylim(-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
ax.set_aspect('auto')
# Background
ax.add_patch(Rectangle((0,0),1,1,facecolor=(0.6,0.6,0.6,1),fill=True,zorder=1))
# Draw lines of latitude and longitude
for lat in range(-90,95,5):
lwd=0.75
x=[]
y=[]
for lon in range(-180,181,1):
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(lon),
numpy.array(lat),
args.pole_longitude,
args.pole_latitude)
nx=rp[0]+args.npg_longitude
if nx>180: nx -= 360
ny=rp[1]
if(len(x)==0 or (abs(nx-x[-1])<10 and abs(ny-y[-1])<10)):
x.append(nx)
y.append(ny)
else:
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
x=[]
y=[]
if(len(x)>1):
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
for lon in range(-180,185,5):
lwd=0.75
x=[]
y=[]
for lat in range(-90,90,1):
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(lon),
numpy.array(lat),
args.pole_longitude,
args.pole_latitude)
nx=rp[0]+args.npg_longitude
if nx>180: nx -= 360
ny=rp[1]
if(len(x)==0 or (abs(nx-x[-1])<10 and abs(ny-y[-1])<10)):
x.append(nx)
y.append(ny)
else:
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
x=[]
y=[]
if(len(x)>1):
ax.add_line(Line2D(x, y, linewidth=lwd, color=(0.4,0.4,0.4,1),
zorder=10))
# Plot the land mask
mask_pc=plot_cube(0.05,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
mask = mask.regrid(mask_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
lats = mask.coord('latitude').points
lons = mask.coord('longitude').points
mask_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, mask.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(
((0.2,0.2,0.2,0),
(0.2,0.2,0.2,1))),
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
alpha=0.1,
zorder=500)
# Plot the T2M
t2m_pc=plot_cube(0.05,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
t = t.regrid(t2m_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
# Adjust to show the wind
wscale=200
s=wind_noise_field.data.shape
wind_noise_field.data=qcut(wind_noise_field.data.flatten(),wscale,labels=False,
duplicates='drop').reshape(s)-(wscale-1)/2
# Plot as a colour map
wnf=wind_noise_field.regrid(t,iris.analysis.Linear())
t2m_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, t.data*1000+wnf.data,
cmap='RdYlBu_r',
alpha=0.8,
zorder=100)
# Plot the precip
precip_pc=plot_cube(0.25,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
precip = precip.regrid(precip_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
wnf=wind_noise_field.regrid(precip,iris.analysis.Linear())
precip.data[precip.data>0.8] += wnf.data[precip.data>0.8]/3000
precip.data[precip.data<0.8] = 0.8
cols=[]
for ci in range(100):
cols.append([0.0,0.3,0.0,ci/100])
precip_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, precip.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(cols),
alpha=0.9,
zorder=200)
# Plot the observations locations
def plot_obs(obs,alpha):
for i in range(width):
for j in range(height):
if obs.mask[i,j]: continue
rp=iris.analysis.cartography.rotate_pole(numpy.array(i_to_x(i)),
numpy.array(j_to_y(j)),
180,
90)
nlon=rp[0][0]
nlat=rp[1][0]
ax.add_patch(matplotlib.patches.Circle((nlon,nlat),
radius=0.25,
facecolor='black',
edgecolor='black',
linewidth=0.1,
alpha=alpha*obs[i,j],
zorder=180))
plot_obs(get_obs(dte),1)
# Plot the fog of ignorance
fog_pc=plot_cube(0.25,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
fog = fog.regrid(precip_pc,iris.analysis.Linear())
cols=[]
def fog_map(x):
return 1/(1+math.exp((x-0.5)*-10))
for ci in range(100):
cols.append([0.8,0.8,0.8,fog_map(ci/100)])
fog_img = ax.pcolorfast(lons, lats, fog.data,
cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(cols),
alpha=0.95,
zorder=300)
# Label with the date
ax.text(180/args.zoom-(360/args.zoom)*0.009,
90/args.zoom-(180/args.zoom)*0.016,
"%04d-%02d-%02d" % (args.year,args.month,args.day),
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='top',
color='black',
bbox=dict(facecolor=(0.6,0.6,0.6,0.5),
edgecolor='black',
boxstyle='round',
pad=0.5),
size=14,
clip_on=True,
zorder=500)
# Render the figure as a png
fig.savefig('%s/%04d%02d%02d%02d%02d.png' % (args.opdir,args.year,
args.month,args.day,
int(args.hour),
int(args.hour%1*60)))
That script uses a random noise field to generate the wind vectors, and we want every frame to use the same noise field, so make and store that.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Make a fixed noise field for wind-map plots.
import os
import iris
import numpy
import pickle
import os
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--resolution", help="Resolution for plot grid",
default=0.1,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--zoom", help="Scale factor for viewport (1=global)",
default=1,type=float,required=False)
parser.add_argument("--opfile", help="Output (pickle) file name",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_time_skips/z.pkl" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.dirname(args.opfile)):
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(args.opfile))
# Nominal projection
cs=iris.coord_systems.RotatedGeogCS(90,180,0)
def plot_cube(resolution,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax):
lat_values=numpy.arange(ymin,ymax+resolution,resolution)
latitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lat_values,
standard_name='latitude',
units='degrees_north',
coord_system=cs)
lon_values=numpy.arange(xmin,xmax+resolution,resolution)
longitude = iris.coords.DimCoord(lon_values,
standard_name='longitude',
units='degrees_east',
coord_system=cs)
dummy_data = numpy.zeros((len(lat_values), len(lon_values)))
plot_cube = iris.cube.Cube(dummy_data,
dim_coords_and_dims=[(latitude, 0),
(longitude, 1)])
return plot_cube
z=plot_cube(args.resolution,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
(width,height)=z.data.shape
z.data=numpy.random.rand(width,height)-0.5
z2=plot_cube(args.resolution*2,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
(width,height)=z2.data.shape
z2.data=numpy.random.rand(width,height)-0.5
z2=z2.regrid(z,iris.analysis.Linear())
z.data=z.data+z2.data
z4=plot_cube(args.resolution*4,-180/args.zoom,180/args.zoom,
-90/args.zoom,90/args.zoom)
(width,height)=z4.data.shape
z4.data=numpy.random.rand(width,height)-0.5
z4=z4.regrid(z,iris.analysis.Linear())
z.data=z.data+z4.data*100
pickle.dump( z, open( args.opfile, "wb" ) )
To make the video, it is necessary to run the frame generation script above hundreds of times - giving an image for every hour. This script makes the list of commands needed to make all the images, which can be run in parallel.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Scripts to make a 20CRv3 plot for a range of days
import os
import datetime
years=(1850,1860,1870,1880,1891,1901,1911,1921,1932,
1942,1952,1963,1973,1983,1993,2004,2014)
ycount=0
current = datetime.datetime(years[ycount],3,1,0)
count=0
while ycount<len(years):
opf = "%s/images/20CRv3_time_skips/%04d%02d%02d%02d00.png" %\
(os.getenv('SCRATCH'),current.year,
current.month,current.day,current.hour)
if not os.path.isfile(opf):
print("./20CRv3_released.py --year=%d --month=%d --day=%d --hour=%d" %
(current.year,current.month,current.day,current.hour))
current += datetime.timedelta(hours=1)
count = count+1
if count>=240:
count=0
ycount+=1
if ycount<len(years):
current = datetime.datetime(years[ycount],3,1,0)
There is a discontinuity in the video at each of the time skips, which would be visually jarring. These two scripts smooth these discontinuities by adding a few interpolated frames between the end of one time period and the start of the next.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Take two images, and make a series of images interpolating
# between them to provide a dissolve transition.
import os, numpy, PIL
from PIL import Image
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--startfile",
type=str,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--endfile",
type=str,required=True)
parser.add_argument("--n", help="No. of interpolating images",
type=int,default=12)
parser.add_argument("--opdir", help="Directory for files",
default="%s/images/20CRv3_time_skips" % \
os.getenv('SCRATCH'),
type=str,required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
startarr=numpy.array(Image.open("%s/%s" % (args.opdir,args.startfile)),
dtype=numpy.float)
endarr=numpy.array(Image.open("%s/%s" % (args.opdir,args.endfile)),
dtype=numpy.float)
for i in range(args.n):
weight=(i+0.5)/args.n
intarr = endarr*weight+startarr*(1-weight)
intarr=numpy.array(numpy.round(intarr),dtype=numpy.uint8)
opfn = "%s/%s.int_%02d.png" % (args.opdir,args.endfile[0:-4],i)
out=Image.fromarray(intarr,mode="RGBA")
out.save(opfn)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Fill in the gaps in the frame list with dissolve transitions.
import os
import datetime
import glob
files = sorted(glob.glob("%s/images/20CRv3_time_skips/[0-9]*.png" %
(os.getenv('SCRATCH'))))
for idx in range(len(files)-1):
f1 = os.path.basename(files[idx])
f2 = os.path.basename(files[idx+1])
d1 = datetime.datetime(int(f1[0:4]),int(f1[4:6]),
int(f1[6:8]),int(f1[8:10]))
d2 = datetime.datetime(int(f2[0:4]),int(f2[4:6]),
int(f2[6:8]),int(f2[8:10]))
if (d2-d1).total_seconds() > 864000:
print(("./make_dissolve_transition.py --startfile=%s "+
"--endfile=%s") % (f1,f2))
To turn the thousands of images into a movie, use ffmpeg
ffmpeg -r 24 -pattern_type glob -i 20CRv3_time_skips/\*.png \
-c:v libx264 -threads 16 -preset slow -tune film \
-profile:v high -level 4.2 -pix_fmt yuv420p \
-b:v 5M -maxrate 5M -bufsize 20M \
-c:a copy 20CRv3_time_skips.mp4